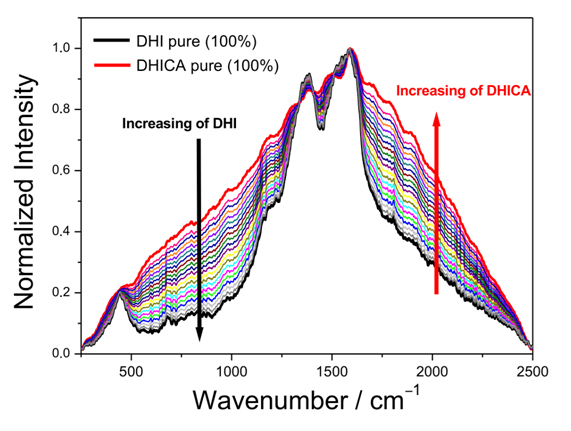
Eumelanins are large polymers composed of 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) and 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA). ROS generation is higher during the synthesis of DHI than during the synthesis of DHICA, thus the production of eumelanins with high relative DHI contents may compromise the viability of cells and organisms. Here it is shown that dispersive Raman spectroscopy allows a non-invasive direct detection and quantification of DHI and DHICA in unaltered eumelanins that can be applied to the analysis of natural pigments in biological tissues. Using synthetic eumelanins purely composed of DHI or DHICA, a model is developed to determine the differential contribution of these subunits to the Raman spectra of mixed eumelanins, and exemplify the predictive capacity of the model with natural eumelanins deposited in black and grey feathers of fowl. The wavenumber ranges of 550-1200 cm-1 and 1650-2300 cm-1 were found significant to predict the DHI:DHICA ratio in unknown samples. informacion[at]ebd.csic.es Galván et al (2018) Raman spectroscopy quantification of eumelanin subunits in natural unaltered pigments. PIGM CELL MELANOMA R https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.12707
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/pcmr.12707
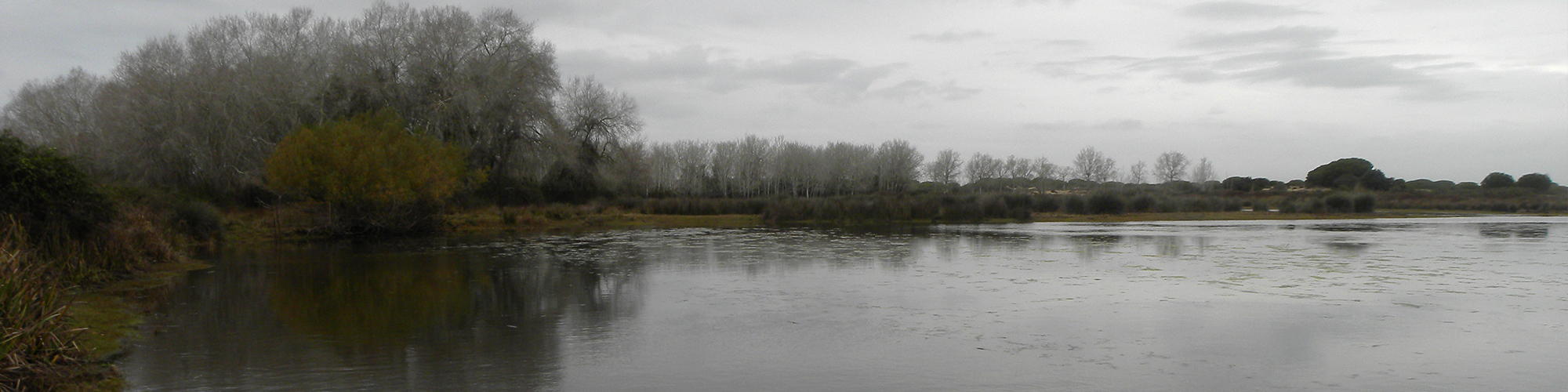







 Las altas temperaturas están provocando que las lagunas y las marismas de Doñana pierdan agua rápidamente
Las altas temperaturas están provocando que las lagunas y las marismas de Doñana pierdan agua rápidamente



