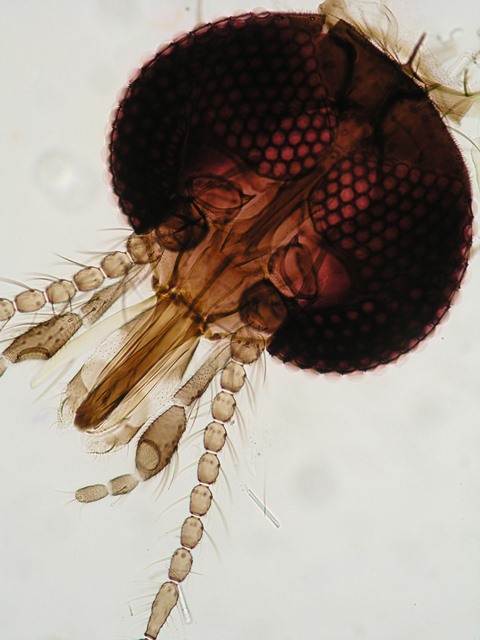
Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) are vectors of pathogens that affect wildlife, livestock and, occasionally, humans. Culicoides imicola (Kieffer, 1913) is considered to be the main vector of the pathogens that cause bluetongue disease (BT) and African horse sickness (AHS) in southern Europe. The study of blood-feeding patterns in Culicoides is an essential step towards understanding the epidemiology of these pathogens. Molecular tools that increase the accuracy and sensitivity of traditional methods have been developed to identify the hosts of potential insect vectors. However, to the present group's knowledge, molecular studies that identify the hosts of C. imicola in Europe are lacking. The present study genetically characterizes the barcoding region of C. imicola trapped on farms in southern Spain and identifies its vertebrate hosts in the area. The report also reviews available information on the blood-feeding patterns of C. imicola worldwide. Culicoides imicola from Spain feed on blood of six mammals that include species known to be hosts of the BT and AHS viruses. This study provides evidence of the importance of livestock as sources of bloodmeals for C. imicola and the relevance of this species in the transmission of BT and AHS viruses in Europe. informacion[at]ebd.csic: Martínez-de la Puente et al (2017) First molecular identification of the vertebrate hosts of Culicoides imicola in Europe and a review of the blood-feeding patterns worldwide: implications for the transmission of Bluetongue disease and African Horse Sickness. Medical and Veterinary Entomology. Doi 10.1111/mve.12247
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/mve.12247/full







 Open Call for Research Projects in ICTS-Doñana!
Open Call for Research Projects in ICTS-Doñana!


